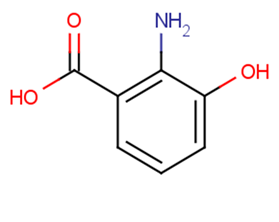
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid
CAS No. 548-93-6
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid( 3-HYDROXY-2-AMINOBENZOIC ACID )
Catalog No. M19626 CAS No. 548-93-6
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid also known as 2-amino-3-hydroxy-benzoate or 3-ohaa belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid has been found in human epidermis and bladder tissues and has also been detected in multiple biofluids such as urine and blood.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 59 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid also known as 2-amino-3-hydroxy-benzoate or 3-ohaa belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid has been found in human epidermis and bladder tissues and has also been detected in multiple biofluids such as urine and blood.
-
Description3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid also known as 2-amino-3-hydroxy-benzoate or 3-ohaa belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid has been found in human epidermis and bladder tissues and has also been detected in multiple biofluids such as urine and blood. Within the cell 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid is primarily located in the cytoplasm. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid exists in all eukaryotes ranging from yeast to humans. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid and L-alanine can be biosynthesized from L-3-hydroxykynurenine; which is catalyzed by the enzyme kynureninase. Furthermore 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid can be converted into cinnavalininate through its interaction with the enzyme catalase. Furthermore L-Alanine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid can be biosynthesized from 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine through its interaction with the enzyme kynureninase. Furthermore 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid can be converted into 2-amino-3-carboxymuconic acid semialdehyde; which is catalyzed by the enzyme 3-hydroxyanthranilate 34-dioxygenase. Furthermore 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid can be converted into 2-amino-3-carboxymuconic acid semialdehyde through the action of the enzyme 3-hydroxyanthranilate 34-dioxygenase. Finally L-Alanine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid can be biosynthesized from 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine; which is mediated by the enzyme kynureninase. In humans 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid is involved in the tryptophan metabolism pathway.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms3-HYDROXY-2-AMINOBENZOIC ACID
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
Recptorothers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number548-93-6
-
Formula Weight153.14
-
Molecular FormulaC7H7NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10uM
-
SMILESNc1c(O)cccc1C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Antoni A D Rubaltelli F F Costa C et al. Effect of phototherapy on the urinary excretion of tryptophan metabolites in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.[J]. Acta Vitaminologica Et Enzymologica 1975 29(1-6):145.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3,5-Dimethylbenzalde...
3,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, inhibiting Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas albicans, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
-
(+)-Longifolene
(+)-Longifolene is a naturally occurring.
-
1-Methylxanthine
1-Methylxanthine is a caffeine derivative. 1-Methylxanthine is an essential human urinary metabolite of caffeine and theophylline (1,3-dimethylxanthine, TP).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


